Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: The Silent Revolution in Automotive Technology
In the realm of automotive innovation, a groundbreaking technology is quietly reshaping the future of transportation. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, once relegated to the realm of science fiction, are now emerging as a viable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional combustion engines. This article delves into the fascinating world of hydrogen-powered cars, exploring their potential to revolutionize the automotive industry and pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future on our roads.

The Science Behind Hydrogen Fuel Cells
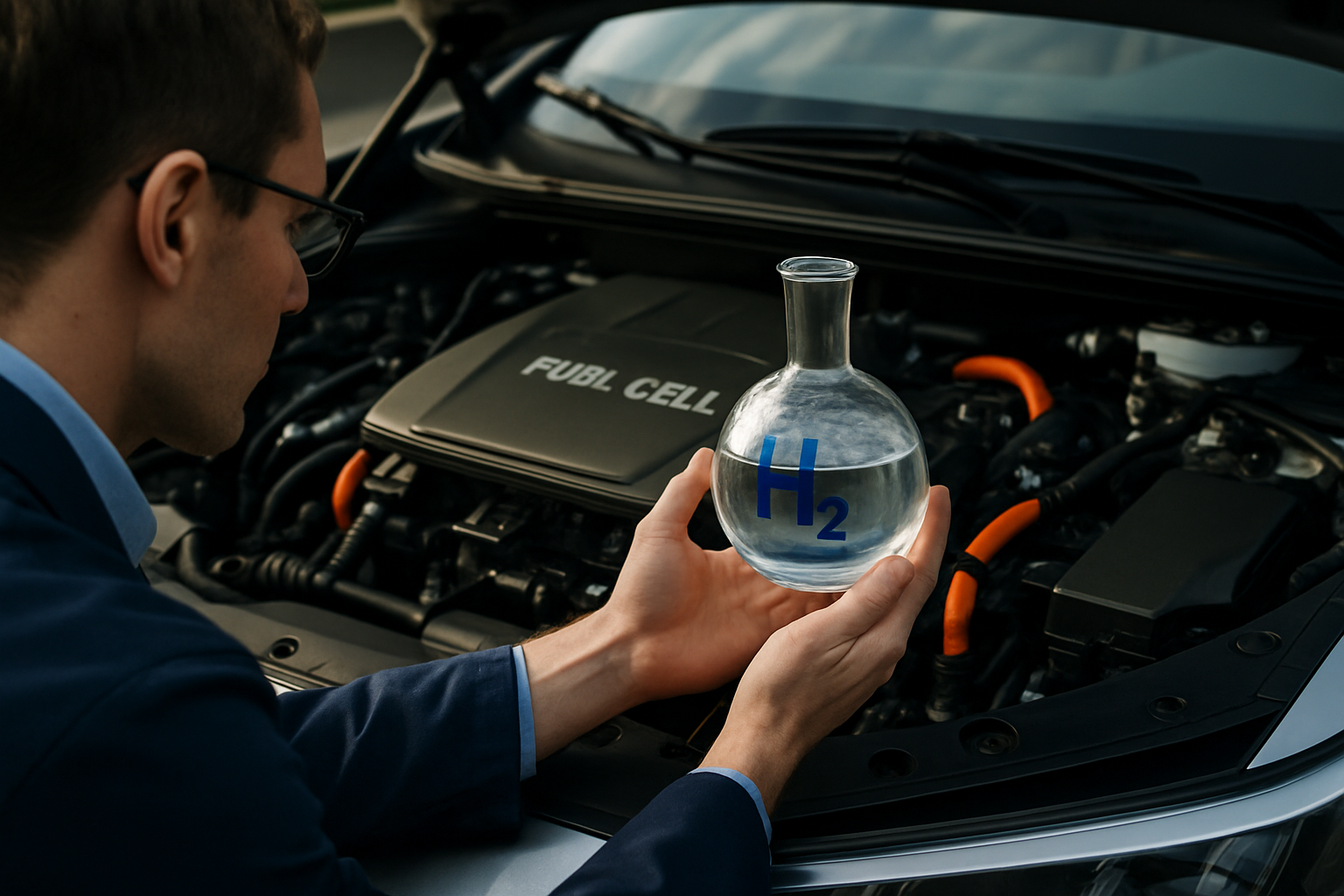
At the heart of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles lies a remarkable feat of engineering. Unlike traditional internal combustion engines, fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. This process, known as reverse electrolysis, produces only water and heat as byproducts, making it an incredibly clean energy source.
The fuel cell stack, composed of multiple individual cells, acts as the powerhouse of these vehicles. Each cell contains an anode, cathode, and electrolyte membrane. Hydrogen is fed into the anode, where it’s split into protons and electrons. The protons pass through the electrolyte membrane to the cathode, while the electrons are forced through an external circuit, generating electricity to power the vehicle’s electric motor.
Infrastructure and Refueling Challenges
One of the primary hurdles facing widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is the lack of infrastructure. Unlike the ubiquitous network of gas stations, hydrogen refueling stations are still relatively scarce. This chicken-and-egg problem has slowed the technology’s growth, as automakers are hesitant to mass-produce vehicles without a robust refueling network, and energy companies are reluctant to invest in stations without a significant number of vehicles on the road.
However, progress is being made. Several countries, including Japan, Germany, and South Korea, have committed to expanding their hydrogen infrastructure. In California, a growing network of hydrogen stations is supporting an increasing number of fuel cell vehicles. As more stations come online, the feasibility of owning and operating a hydrogen-powered car continues to improve.
Performance and Practicality
Contrary to popular belief, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer performance comparable to, and in some cases superior to, conventional gasoline-powered cars. The instant torque provided by electric motors, coupled with the quick refueling times of hydrogen, combines the best aspects of both electric and gasoline vehicles.
Range anxiety, a common concern with battery electric vehicles, is less of an issue with fuel cell cars. Many current models offer ranges of 300 miles or more on a single tank of hydrogen, rivaling their gasoline counterparts. Refueling takes only a few minutes, providing a familiar experience for drivers accustomed to quick pit stops at gas stations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental credentials of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are compelling. With water vapor as the only tailpipe emission, these cars offer a path to truly zero-emission transportation. However, the environmental impact of hydrogen production must also be considered. Currently, most hydrogen is produced through steam methane reforming, a process that still relies on fossil fuels.
The key to maximizing the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cells lies in green hydrogen production. This involves using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power to split water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis. As renewable energy becomes more prevalent and efficient, the potential for a completely clean hydrogen fuel cycle grows ever closer to reality.
Cost Considerations and Market Adoption
As with any emerging technology, the cost of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. The complex technology and materials used in fuel cells contribute to higher production costs compared to conventional vehicles. Additionally, the current price of hydrogen fuel, while competitive with gasoline in some markets, can vary widely depending on production methods and availability.
However, as production scales up and technology improves, costs are expected to decrease. Several major automakers, including Toyota, Honda, and Hyundai, have already introduced fuel cell vehicles to the market, with more models in development. Government incentives and investments in infrastructure are also playing a crucial role in making these vehicles more accessible to consumers.
The Future of Hydrogen in Transportation
Looking ahead, the potential applications for hydrogen fuel cell technology extend far beyond passenger vehicles. Heavy-duty trucks, buses, and even trains are being developed with fuel cell powertrains, offering a promising solution for decarbonizing long-haul transportation and public transit. The maritime industry is also exploring hydrogen as an alternative to heavy fuel oil, with several projects underway to develop hydrogen-powered ships.
As battery technology continues to improve, some may question the need for hydrogen fuel cells in passenger vehicles. However, the rapid refueling capability and long-range potential of hydrogen make it an attractive option for specific use cases, particularly in fleet operations or for consumers who prioritize these features.
The journey towards widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is not without its challenges. Infrastructure development, cost reduction, and scaling up green hydrogen production are all critical hurdles that must be overcome. Yet, the potential benefits – zero-emission transportation, energy security, and reduced dependence on fossil fuels – make this a technology worth pursuing.
As we stand at the crossroads of automotive innovation, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent a fascinating glimpse into a possible future of clean, efficient, and sustainable transportation. While they may not be the sole solution to our environmental challenges, they undoubtedly have a role to play in the diverse ecosystem of future mobility options. The silent revolution of hydrogen fuel cells is underway, and its impact on the automotive landscape promises to be profound and far-reaching.